Plan (noun.)
Definition: An intention or decision about what one is going to do.
Also referenced as: Plans (noun)
Related to: Agreement, Architect, Choice, Intent
Chapter 2: State your Intent | Page 45
Meet Karen.
Karen is a product manager at a startup. Her CEO thinks the key to launching their product in a crowded market is a sleek look and feel.
Karen recently conducted research to test the product with its intended users. With the results in hand, she worries that what the CEO sees as sleek is likely to seem cold to the users they want to reach.
Karen has research on her side, but she still needs to define what good means for her organization. Her team needs to state their intent.
To establish an intent, Karen talks with her CEO about how their users’ aesthetic wants don’t line up with the look and feel of the current product.
She starts their conversation by confirming that the users from her research are part of the intended audience for the product.
Next, she helps the CEO create a list of questions and actions the research brought up.
Afterwards, Karen develops a plan for communicating her findings to the rest of the team.
Chapter 3: Face Reality | Page 61
Rhetoric matters.
Rhetoric is communication designed to have a persuasive effect on its audience.
Here are some common rhetorical reasons for making diagrams and maps:
- Reflection: Point to a future problem (e.g., a map of a local landfill’s size in the past, present, and projected future).
- Options: Show something as it could be (e.g., a diagram showing paths a user could take to set up an application).
- Improvements: Show something as it should be (e.g., a diagram pointing out opportunities found during user research).
- Identification: Show something as it once was or is today (e.g., a map of your neighborhood).
- Plan: Show something as it will be (e.g., a map of your neighborhood with bike lanes).
Chapter 3: Face Reality | Page 68
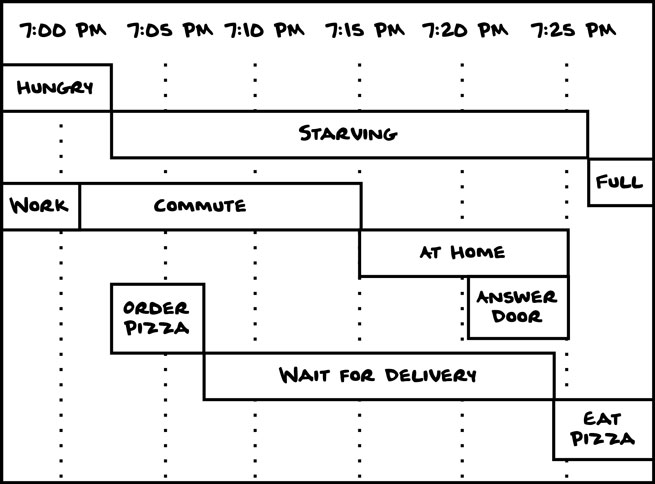
3. Gantt Chart
A Gantt chart depicts how processes relate to one another over time. Timelines, and project plans are both common examples of Gantt charts.
This type of chart helps us to understand relationships between people, tasks, and time.
Chapter 4: Choose a Direction | Page 102
Admit where you are.
Let’s say you’re on a weeklong bicycle trip. You planned to make it to your next stop before dark, but a flat tire delayed you by a few hours.
Even though you planned to get further along today, the truth is that pursuing that plan would be dangerous now.
Similarly, an idea you can draw on paper in one day may end up taking you a lifetime to make real. With the ability to make plans comes great responsibility.
Think about what you can do with the time and resources you have. Filtering and being realistic are part of the job. Keep reevaluating where you are in relation to where you want to go.
Be careful not to fall in love with your plans or ideas. Instead, fall in love with the effects you can have when you communicate clearly.
Chapter 6: Play with Structure | Page 128
Sorting is easier than deciding how to sort.
Sorting is the act of arranging content according to established rules. The act of deciding how to sort something within a taxonomy is called classification.
If you have a large pile of things, it may take a lot of time to sort through them. But sorting isn’t the hard part. Classification is.
Think about sorting a bag of groceries into a pre-arranged pantry. Everything has a place. You’re simply following the plan. Easy, right?
Now unload that same bag into a kitchen without rules for where things go. How much longer would it take you? How much more frustrating a task would it be? How much variation would you get when the next person unloads groceries?
Sorting is easy when clear rules are in place. But without those rules, assumptions take over and things end up in places where they can be harder to find.
The most challenging part of classification is working with other people to agree on a set of rules.
Chapter 6: Play with Structure | Page 132
Facets are the lenses we use to classify.
A facet is a discrete piece of knowledge you can use to classify something. The more facets something has, the more ways it can be organized.
Using the record store as an example, the following facets are available for each record:
- Record Name
- Artist Name
- Record Label
- Length
- Release Date
- Price
If a particular facet is interesting but the data to support it doesn’t exist or is hard to gather, it might not be the best plan to use that facet.
For example, finding out which instrument models were used on each album may be interesting, but it is also likely to be quite time-consuming to collect.
Chapter 7: Prepare to Adjust | Page 148
Adjustments are a part of reality.
From moment to moment, the directions we choose forever change the objects we make, the effects we see, and the experiences we have.
As we move towards our goals, things change and new insights become available. Things always change when we begin to understand what we couldn’t make sense of before. As a sensemaker, the most important skill you can learn is to adjust your course to accommodate new forces as you encounter them on your journey.
Don’t seek finalization. Trying to make something that will never change can be super frustrating. Sure, it’s work to move those boxes and arrows around as things change. But that is the work, not a reason to avoid making a plan. Taking in feedback from other people and continuously refining the pieces as well as the whole is what assures that something is “good.”
Don’t procrastinate. Messes only grow with time. You can easily make excuses and hold off on doing something until the conditions are right, or things seem stable.
Perfection isn’t possible, but progress is.
